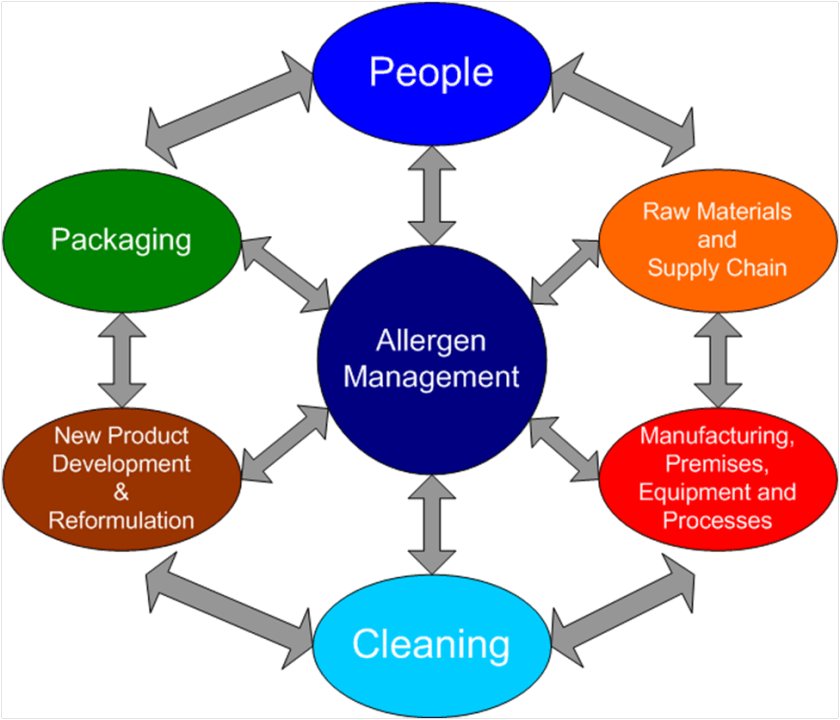
A food allergen policy is a crucial document or set of guidelines designed to ensure the safety of individuals who may be at risk of allergic reactions due to food consumption. This policy outlines the procedures and precautions a food business must follow to manage and minimize allergen-related risks effectively. By implementing a robust allergen policy, a business not only demonstrates its commitment to customer safety but also adheres to regulatory requirements aimed at preventing allergenic incidents.
Why is a Food Allergen Policy Important?
Food allergen policies are vital for several reasons:
- Customer Safety: They help protect customers with food allergies or intolerances by ensuring that allergens are properly identified and managed.
- Regulatory Compliance: They ensure adherence to food safety regulations and legislation, reducing the risk of legal penalties and enhancing business credibility.
- Staff Training: They provide guidance on how to handle allergens safely, ensuring that staff are well-informed and capable of managing allergen risks.
- Reputation Management: A well-implemented allergen policy builds trust with customers, demonstrating that the business takes allergen safety seriously and is committed to preventing incidents.
- Prevention of Allergic Reactions: By implementing appropriate procedures, the policy helps prevent potentially severe or even fatal allergic reactions.
The Importance of an Allergen Policy in the Food Industry
In the food industry, where products are consumed directly, the risk of allergic reactions can have serious consequences. An allergen policy underscores a business’s dedication to food safety and ensures that both staff and customers are protected.
- Compliance with Regulations: Food allergen policies help businesses meet legal requirements, avoiding potential fines and sanctions. This compliance is not only a legal obligation but also a key aspect of maintaining customer trust.
- Customer Assurance: Customers feel reassured knowing that a business has clear procedures for managing allergens, which can enhance their overall dining experience and loyalty.
- Staff Training and Guidance: The policy serves as a training tool, guiding staff on best practices for handling allergens and ensuring consistent adherence to safety protocols.
Owen’s Law and Its Impact
Owen’s Law emerged from the tragic death of Owen Carey, who suffered a fatal anaphylactic reaction after consuming a meal with undisclosed allergens. This incident highlighted the need for clear allergen information on menus and spurred legislative changes to improve allergen communication in the food industry. The Food Standards Agency (FSA) has since supported measures to make allergen labeling mandatory, aiming to prevent such tragedies and enhance food safety.
Key Components of a Food Allergen Policy
A comprehensive food allergen policy should include the following elements:
- Purpose of the Policy: Clearly state the objectives and scope of the policy, emphasizing the commitment to allergen safety and customer well-being.
- The 14 Food Allergens: List the 14 allergens identified by legislation, such as peanuts, tree nuts, milk, eggs, fish, and others. This list provides a reference for identifying potential allergens in food products.
- Allergy Labelling Legislation and Regulations: Detail the relevant laws and regulations regarding allergen labeling and how the business complies with these requirements. This section should cover both local and international standards if applicable.
- Business Commitment: Outline the measures taken by the business to ensure allergen safety, including staff training, ingredient sourcing, and food preparation procedures.
- Background Information: Provide an overview of food allergens, intolerances, and the risks associated with them. This section should explain how allergens can affect individuals and the importance of proper management.
- Responsibilities: Define the roles and responsibilities of key personnel in managing allergens. This includes senior leadership, kitchen staff, and service staff, ensuring that everyone understands their role in maintaining allergen safety.
- Allergen Information Management: Describe how allergen information is gathered, documented, and updated. This includes procedures for recording ingredient information, supplier details, and staff training records.
- Customer Communication: Explain how allergen information is communicated to customers, including how staff should respond to allergen-related inquiries and how allergen information is displayed on menus and labels.
- Procedures and Precautions: Detail the procedures for managing allergens in the kitchen, including storage, preparation, and serving. This section should also cover cleaning procedures to prevent cross-contamination.
- Emergency Procedures: Provide clear instructions for handling allergen-related emergencies, such as how to respond to a severe allergic reaction and the steps to take in such situations.
- Inclusivity: Describe how the business accommodates customers with food allergies and intolerances, ensuring that they are considered in menu planning and service.
Summary
A food allergen policy is an essential tool for any business involved in food production, distribution, or service. It demonstrates a commitment to customer safety and regulatory compliance by outlining clear procedures for managing allergens. By including detailed information on allergen identification, handling procedures, and emergency protocols, a well-crafted policy helps prevent allergic reactions and builds trust with customers. With the backing of legislative changes like Owen’s Law, businesses are better equipped to ensure that allergen information is accurately communicated, further protecting individuals with food allergies and contributing to overall food safety.