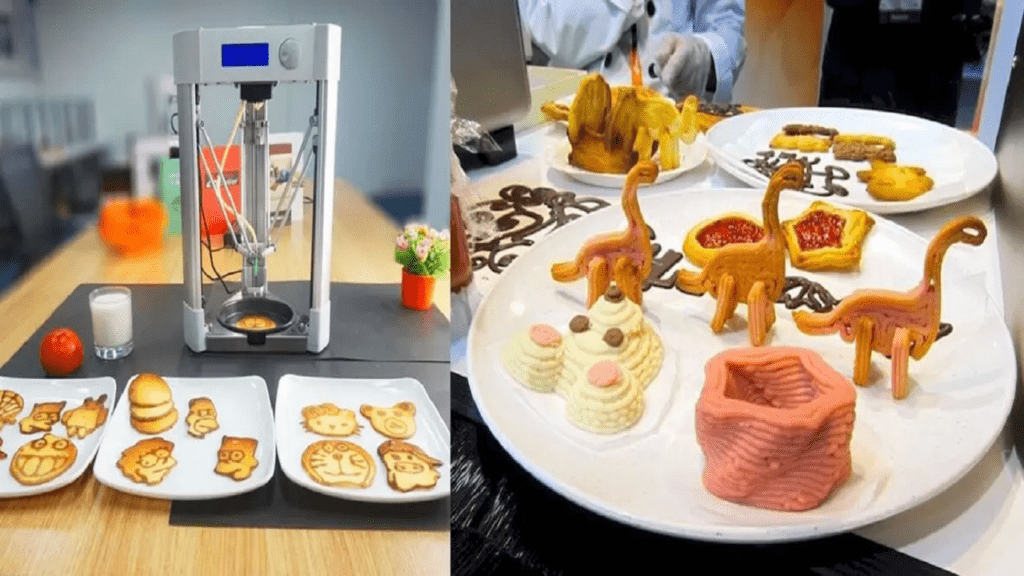
3D food printing is a groundbreaking technology that is reshaping the food industry by merging culinary arts with advanced manufacturing. This innovative approach allows for the precise, layer-by-layer construction of food items using a variety of ingredients and materials. By leveraging digital designs and automated processes, 3D food printing offers a new dimension of creativity and efficiency in food production, promising to revolutionize how we create, consume, and think about food.
What is 3D Food Printing?
3D food printing involves using specialized printers to produce food items based on digital recipes or designs. Similar to traditional 3D printing, which builds objects layer by layer using materials like plastic or metal, 3D food printing constructs edible items by extruding layers of food ingredients. The process can use various materials, including pureed fruits, vegetables, proteins, and doughs, to create complex shapes and textures.
Benefits of 3D Food Printing
- Customization and Personalization
- Tailored Nutrition: 3D food printing allows for the creation of personalized meals that meet specific dietary needs and preferences. Nutrient profiles can be adjusted based on individual health requirements.
- Creative Design: The technology enables the creation of intricate and visually appealing food designs that would be challenging to achieve with traditional methods.
- Efficiency and Waste Reduction
- Reduced Waste: 3D food printing uses ingredients more efficiently by precisely controlling the amount of material used, reducing food waste.
- Streamlined Production: The technology simplifies complex food preparation processes, allowing for faster production and more efficient use of kitchen resources.
- Innovative Food Experiences
- Unique Textures and Shapes: 3D printing enables the creation of novel textures and shapes that are not possible with conventional cooking techniques.
- Interactive Dining: The technology can be used to create interactive dining experiences, such as customized meal components or personalized food items.
- Enhanced Sustainability
- Alternative Ingredients: 3D food printing can incorporate alternative and sustainable ingredients, such as insect proteins or lab-grown meat, supporting more eco-friendly food production practices.
- Energy Efficiency: The precise nature of the printing process can reduce the energy required for food production compared to traditional methods.
- Medical and Therapeutic Applications
- Customized Nutritional Solutions: 3D food printing can create specialized meals for individuals with medical conditions or dietary restrictions, such as texture-modified diets for those with swallowing difficulties.
- Functional Foods: The technology allows for the incorporation of functional ingredients, such as vitamins and minerals, into food items for specific health benefits.
Applications of 3D Food Printing
- Gourmet Cuisine
- Artistic Presentation: Chefs and culinary artists use 3D food printing to craft elaborate and aesthetically pleasing dishes, pushing the boundaries of food design and presentation.
- Innovative Recipes: The technology enables the creation of new recipes and flavor combinations that are not possible with traditional cooking methods.
- Food Production and Manufacturing
- Customizable Products: Food manufacturers use 3D printing to produce customized food items for specific markets or customer preferences, such as personalized chocolates or bespoke confectionery.
- Efficient Production: The technology streamlines production processes, making it easier to produce complex food products on a large scale.
- Healthcare and Nutrition
- Specialized Diets: Hospitals and care facilities use 3D food printing to create specialized diets for patients with specific nutritional needs, such as those with swallowing difficulties or dietary restrictions.
- Nutritional Supplements: The technology enables the incorporation of nutritional supplements into food items, providing additional health benefits.
- Education and Research
- Culinary Education: Culinary schools and research institutions use 3D food printing to explore new cooking techniques and ingredient combinations, enhancing culinary education and innovation.
- Food Science Research: Researchers study the impact of different ingredients and printing techniques on food quality, texture, and nutritional content.
- Consumer Markets
- Personalized Foods: Consumers can use 3D food printing to create personalized foods at home, such as custom-shaped cookies or tailored nutritional snacks.
- Interactive Cooking: The technology offers a new way for consumers to engage with food preparation, allowing for hands-on creation of unique and customized food items.
Challenges of 3D Food Printing
- Technical and Engineering Limitations
- Ingredient Compatibility: Not all food ingredients are suitable for 3D printing, and developing new formulations that work with the technology can be challenging.
- Printer Limitations: The capabilities of 3D food printers can vary, with limitations in print speed, resolution, and material handling.
- Cost and Accessibility
- High Initial Costs: The cost of 3D food printers and associated equipment can be high, making the technology less accessible for some businesses and consumers.
- Ingredient Costs: Specialized ingredients and formulations for 3D printing may be more expensive than traditional food ingredients.
- Regulatory and Safety Concerns
- Food Safety: Ensuring that 3D-printed foods meet food safety standards and regulations is crucial, as the technology introduces new variables into food production.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations and standards for 3D-printed food products, requiring careful compliance and adaptation.
- Consumer Acceptance
- Perception: Some consumers may be hesitant to embrace 3D-printed foods due to concerns about taste, texture, or the unfamiliarity of the technology.
- Education: Educating consumers about the benefits and safety of 3D-printed foods is essential for widespread adoption.
- Sustainability
- Material Waste: While 3D food printing can reduce waste in some areas, the production of printing materials and the technology itself may have environmental impacts.
- Resource Use: The energy and resources required for 3D food printing must be considered in the context of overall sustainability.
Future Trends in 3D Food Printing
- Advancements in Ingredients and Materials
- New Formulations: Continued research and development will lead to new ingredient formulations and materials that expand the capabilities of 3D food printing.
- Sustainable Ingredients: The use of sustainable and alternative ingredients, such as plant-based proteins or lab-grown meat, will become more common.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning
- Smart Printing: AI and machine learning will enhance the precision and efficiency of 3D food printing, enabling adaptive and intelligent food creation processes.
- Predictive Analytics: Data-driven insights will optimize printing techniques and ingredient combinations, improving overall food quality.
- Customization and Personalization
- Personalized Nutrition: Advances in personalized nutrition will enable more tailored and customized food products, catering to individual dietary needs and preferences.
- Interactive Experiences: The technology will continue to offer innovative and interactive dining experiences, enhancing consumer engagement and satisfaction.
- Expansion into New Markets
- Consumer Products: 3D food printing will become more accessible for home use, allowing consumers to create personalized and customized foods in their own kitchens.
- Emerging Markets: The technology will expand into new markets and regions, offering opportunities for growth and innovation in the global food industry.
- Regulatory Developments
- Standards and Guidelines: As 3D food printing becomes more prevalent, regulatory bodies will develop standards and guidelines to ensure food safety and quality.
- Global Harmonization: Efforts will be made to harmonize regulations and standards across different regions, facilitating international trade and adoption.
Conclusion
3D food printing represents a significant leap forward in food production and culinary arts, offering unprecedented opportunities for customization, efficiency, and innovation. While the technology presents challenges such as cost, technical limitations, and consumer acceptance, its potential to revolutionize food creation and consumption is immense. By continuing to advance ingredient formulations, integrate with AI, and expand into new markets, 3D food printing is poised to play a transformative role in the future of the food industry, enhancing the way we think about and experience food.